Difference between revisions of "The History of Scientific Publishing"
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
According to Wikipedia's [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timeline_of_scientific_experiments Timeline of scientific experiments] the first such experiment was conducted by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Empedocles Empedocles] in the 5th century BC some 2.500 years ago. Personally i do not share this view of history after having read [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Dawn_of_Everything The Dawn of Everything] which outlines how much human activity of the past is being ignored by todays accounts just because people did not have the tools to communicate their findings in a way that preserved it for future generations in the original code. | According to Wikipedia's [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timeline_of_scientific_experiments Timeline of scientific experiments] the first such experiment was conducted by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Empedocles Empedocles] in the 5th century BC some 2.500 years ago. Personally i do not share this view of history after having read [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Dawn_of_Everything The Dawn of Everything] which outlines how much human activity of the past is being ignored by todays accounts just because people did not have the tools to communicate their findings in a way that preserved it for future generations in the original code. | ||
| − | + | == Oral Scientific Communication ~100.000 years ago == | |
So lets imagine some [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human] being of the far past say 100.000 ore more years ago conducting something we would call a scientific experiment these days, e.g. trying out [http://www.visual-arts-cork.com/artist-paints/prehistoric-colour-palette.htm different ways of coloring clay] for body painting and later wall murals. | So lets imagine some [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human] being of the far past say 100.000 ore more years ago conducting something we would call a scientific experiment these days, e.g. trying out [http://www.visual-arts-cork.com/artist-paints/prehistoric-colour-palette.htm different ways of coloring clay] for body painting and later wall murals. | ||
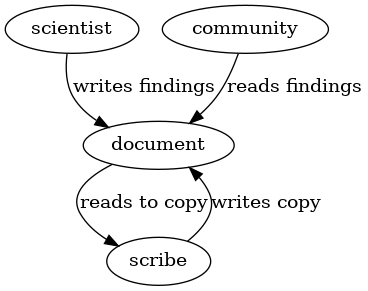
The "scienfific communication" in this case would have been based on [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Origin_of_language oral/vocal/language] which is these days is assumed to be well established in the human community at the time. | The "scienfific communication" in this case would have been based on [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Origin_of_language oral/vocal/language] which is these days is assumed to be well established in the human community at the time. | ||
| − | + | ||
<graphviz format='svg'> | <graphviz format='svg'> | ||
digraph s10000 { | digraph s10000 { | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
scientist -> document [ label="writes findings"] | scientist -> document [ label="writes findings"] | ||
community -> document [ label="reads findings" ] | community -> document [ label="reads findings" ] | ||
| + | |||
| + | document -> scribe [ label="reads to copy" ] | ||
| + | scribe -> document [ label="writes copy" ] | ||
} | } | ||
</graphviz> | </graphviz> | ||
| + | |||
== [https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q62108941 Letter of Grand Priest Luenna-AO 4238] == | == [https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q62108941 Letter of Grand Priest Luenna-AO 4238] == | ||
An example clay tablet from the Louvre. | An example clay tablet from the Louvre. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 31: | ||
Printing sped up the process of publication and communication since fare more copies could be created and distributed for far less cost in far shorter time. | Printing sped up the process of publication and communication since fare more copies could be created and distributed for far less cost in far shorter time. | ||
[[File:European_Output_of_Printed_Books_ca._1450–1800.png|640px]] | [[File:European_Output_of_Printed_Books_ca._1450–1800.png|640px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <graphviz format='svg'> | ||
| + | digraph s1000 { | ||
| + | scientist -> document [ label="writes findings"] | ||
| + | community -> document [ label="reads findings" ] | ||
| + | document -> printer [ label="reads to typeset" ] | ||
| + | printer -> printform [ label="typesets" ] | ||
| + | printform -> document [ label="prints copy" ] | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </graphviz> | ||
| + | == Digital Scientific Communication ~50 years ago == | ||
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_publishing Digital publishing] started in the 1970's and was boosted by the availability of Personal Computers, Text processors and the Internet in the next two decades. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The result is an "explosion" of scientific communication with exponential growth rates.[[CiteRef::bornmann2021gr]] | ||
| + | {{#scite: | ||
| + | |reference=bornmann2021gr | ||
| + | |type=journal-article | ||
| + | |title=Growth rates of modern science: a latent piecewise growth curve approach to model publication numbers from established and new literature databases | ||
| + | |authors=Lutz Bornmann;Robin Haunschild;Rüdiger Mutz | ||
| + | |journal=Humanities and Social Sciences Communications | ||
| + | |publisher=Springer Science and Business Media LLC | ||
| + | |issn=2662-9992 | ||
| + | |subject=General Economics, Econometrics and Finance;General Psychology;General Social Sciences;General Arts and Humanities;General Business, Management and Accounting|+sep=; | ||
| + | |volume=8 | ||
| + | |doi=10.1057/s41599-021-00903-w | ||
| + | |year=2021 | ||
| + | |retrieved-from=https://doi.org/ | ||
| + | |retrieved-on=2023-03-04 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <graphviz format='svg'> | ||
| + | digraph s50 { | ||
| + | tpd [ label="textprocessor document" ] | ||
| + | dpd [ label="display document" ] | ||
| + | scientist -> tpd [ label="writes findings with texprocessor e.g. LaTeX/Word"] | ||
| + | tpd -> dpd [ label="renders e.g. to PDF/HTML" ] | ||
| + | community -> dpd [ label="reads findings" ] | ||
| + | dpd -> publisher [ label="submit for publishing" ] | ||
| + | publisher -> dpd [ label="prints/puts online" ] | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </graphviz> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = The need for metadata = | ||
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Everything_Is_Miscellaneous David Weinbergers's Everything is Miscellaneous] nicely explains how the need for indexing the vast amounts of literature (and scientific findings's literature) arose. The solutions to mitigate the problem that were invented in the past few centuries seem not to be fit for the third millenium. | ||
= Links = | = Links = | ||
| Line 47: | Line 95: | ||
|retrieved-on=2023-03-04 | |retrieved-on=2023-03-04 | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | [[Category:Text2KG]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:37, 31 December 2023
According to Wikipedia's Timeline of scientific experiments the first such experiment was conducted by Empedocles in the 5th century BC some 2.500 years ago. Personally i do not share this view of history after having read The Dawn of Everything which outlines how much human activity of the past is being ignored by todays accounts just because people did not have the tools to communicate their findings in a way that preserved it for future generations in the original code.
Oral Scientific Communication ~100.000 years ago
So lets imagine some Human being of the far past say 100.000 ore more years ago conducting something we would call a scientific experiment these days, e.g. trying out different ways of coloring clay for body painting and later wall murals.
The "scienfific communication" in this case would have been based on oral/vocal/language which is these days is assumed to be well established in the human community at the time.

Written Scientific Communication ~5.500 years ago
Clay tablets have been used as the first durable, transportable and copyable means of communication of scientific findings.
Letter of Grand Priest Luenna-AO 4238
An example clay tablet from the Louvre.

Printed Scientific Communication ~1000 years ago
Some 5.000 years the written communication was improved only by modifying the writing medium to papirus and paper, improving the standardization of languages (greek/latin/chinese/ ...) and making the copying a manufacture art as was e.g. the case in christian monasteries. Printing was invented as a mechanized way of copying. Geoffrey Roper - Manuscripts and printing claims that printing was known many centuries befor Gutenberg's invention of the Printing Press
Printing sped up the process of publication and communication since fare more copies could be created and distributed for far less cost in far shorter time.


Digital Scientific Communication ~50 years ago
Digital publishing started in the 1970's and was boosted by the availability of Personal Computers, Text processors and the Internet in the next two decades.
The result is an "explosion" of scientific communication with exponential growth rates.1

The need for metadata
David Weinbergers's Everything is Miscellaneous nicely explains how the need for indexing the vast amounts of literature (and scientific findings's literature) arose. The solutions to mitigate the problem that were invented in the past few centuries seem not to be fit for the third millenium.
Links
References
- ^ Alan Kelly. (2020) "The History and Future of Scientific Publishing" - 10-33 pages. doi: 10.1093/oso/9780190936600.003.0002